Abstract
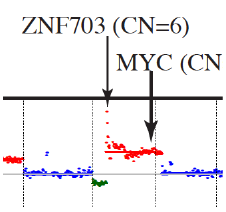
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) sequencing studies could provide novel insights into the molecular pathology of cancer in sub-Saharan Africa. In 15 patient plasma samples collected at the time of diagnosis as part of the Ghana Breast Health Study and unselected for tumor grade and subtype, ctDNA was detected in a majority of patients based on whole- genome sequencing at high (30×) and low (0.1×) depths. Breast cancer driver copy number alterations were observed in the majority of patients.